10 KiB
Compliling and Programming (STM32)
If you are Compling for the Arduino ATmega328p version of the Multiprotocol Module please go to the dedicated Compiling and Programming ATmega328 page.
Multiprotocol source can be compiled using the Arduino IDE using STM32 Core (Maple) and Arduino ARM-Cortex-M3 libraries.
###Install the Arduino IDE and the Multiprotocol project
- Download the Arduino IDE. The currently supported Arduino version is 1.6.5. available for Windows and Mac OSX
- Download the STM32 Core and copy the Arduino_STM32 folder to:
- OSX:
Arduino.app/Contents/Java/hardware(you can open Arduino.app by Ctl Clicking on Arduino.app and selecting "Show Package Contents") - Windows:
C:\Program Files (x86)\Arduino\hardware
- Download the zip file with the Multiprotocol module source code from here
- Unzip and copy the source code folder
Multiprotocolto a folder of your choosing - Click on the
Multiprotocol.ino filein theMultiprotocolfolder and the Arduino environment should appear and the Multiprotocol project will be loaded.
###Prepare the Arduino IDE:
- In order to compile successfully you need also to modify a maple library file. In
....\hardware\Arduino_STM32\STM32F1\cores\maple\libmaple\usart_f1.ccomment out the 2 functions as shown below. This is required to have low-level access to the USART interrupt.
//void __irq_usart2(void) { usart_irq(&usart2_rb, USART2_BASE); }
//void __irq_usart3(void) { usart_irq(&usart3_rb, USART3_BASE); }
- Run the IDE, and on the Tools menu, select Board and then Boards manager. Click on the Arduino DUE (32 Bits ARM-Cortex M3) from the list of available boards. You must do this step, it installs the arm-none-eabi-g++ toolchain!
- Close and reopen the Arduino IDE and load the Multiprotocol project.
- Click on the Verify button to test compile the before you make any changes. If there are errors check the process above and be sure to have the right version of the Arduino IDE.
Common process for OSX and Windows
###Customize the firmware to your hardware and your needs On all modules with STM32F103 microcontroller, the program flash memory on the microcontroller is large enough to accommodate all the protocols. You do not have to make choices on which protocols to upload. Also, it is likely that you used the Banggood 4-in-1 RF module and you will therefore have access to all the RF modules. However, you can follow these instructions to select only a subset protocols.
If you plan to use the PPM mode then you should follow the instructions to customize the protocol selection switch to protocol mapping.
Before customizing your firmware it would be good to review the protocol on the Protocol Details page and to identify the protocols you would like to support on your module.
At the same time make a note of RF modules required by your protocols. For example, if you do not wish to use the FlySky or the Husan protocols then you do not need to compile support the the A7105 RF Module into your firmware. Similarly, if you have no need to bind with ASSAN RC receivers then you do not need to compile the ASSAN protocol into your firmware.
If you plan to use the PPM communication interface with your transmitter, then you need to perform protocol selection with the 16 position switch on your module. This will limit the available protocols you can usefully access in PPM mode on your module to 15 (this limitation does not apply to Serial mode). You should make a list of your 15 chosen protocols, sub protocols and options like this:
| Switch Position | Protocol | Sub-Protocol | Option | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | DSM | DSM2 | 2 | 6 channels @ 22ms |
| 2. | DSM | DSMX | 6 | 6 channels @ 11ms |
| .... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| .... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 15. | FRSKYX | CH_16 | FrSky X receiver 16 chan |
With the above information (required RF modules, selected protocols and 16 pos switch mapping) you are ready to customize your firmware.
All customization is done by editing the _Config.h file in the Multiprotocol Arduino project.
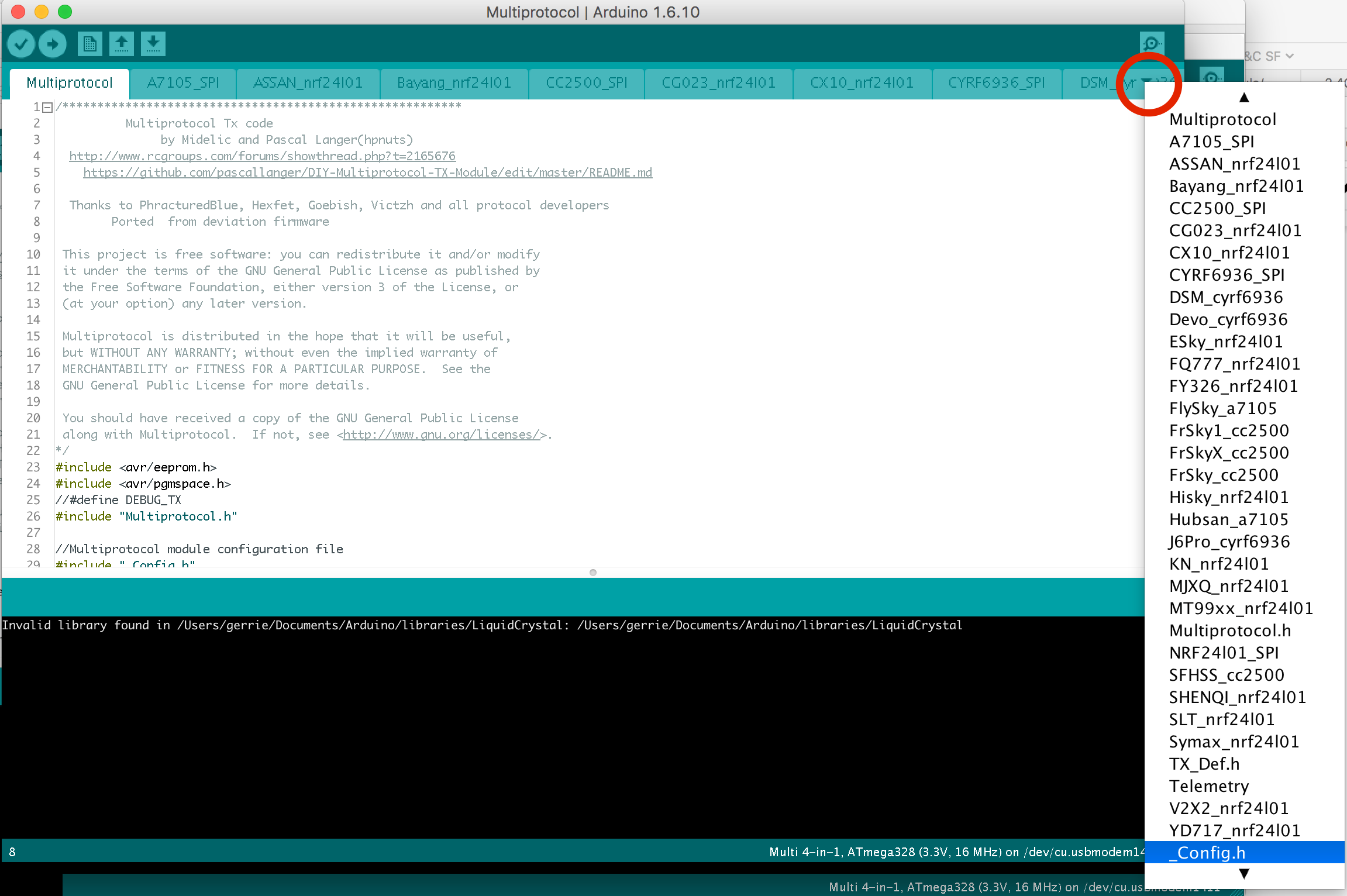
In the Arduino IDE and click on the down arrow on the far right of the tab bar to show a list of project files (see the red circle on the screenshot below). Scroll down and select the _Config.h file.
It is unlikely that you would need to do this, but you can comment out any of the RF modules that you do not need by typing // at the begining of the line that reads :
#define <RF Module name>_INSTALLED . The following line shows the CC2500 module removed
#define A7105_INSTALLED
#define CYRF6936_INSTALLED
//#define CC2500_INSTALLED
#define NFR24L01_INSTALLED
Again it is unlikely that you would want to do this, but you can scroll down to the available protocols and comment out all the protocols you will not require. The following example shows the DEVO protocol commented out.
**
#ifdef CYRF6936_INSTALLED
// #define DEVO_CYRF6936_INO
#define DSM_CYRF6936_INO
#define J6PRO_CYRF6936_INO
#endif**
Look for the line containing #define INVERT_TELEMETRY and make sure that it is uncommented:
#define INVERT_TELEMETRY
Scroll down to the bottom of the file and list your switch mapping to your desired protocol/sub-protocol/options. You typically only need to change the three relevant columns. On models that require a rebind on every start-up (like Syma quads) you can change the NO_AUTOBIND to AUTOBIND .
Finally, if you have not already done so, specify the correct board for the compiler. Under Tools -> Board: select the Generic STM32F103C series board. You can now compile the firmware by clicking on the check mark (Tooltip: Verify) on the menu bar. If everything goes according to plan you should see something like the following line in the lower pane of the window:
Sketch uses 32,464 bytes (99%) of program storage space. Maximum is 32,768 bytes. Global variables use 1,219 bytes (59%) of dynamic memory, leaving 829 bytes for local variables. Maximum is 2,048 bytes.
If you get an error carefully read the error to see the approximate line number where the error occured and correct it.
###Preparing for STM32 microcontroller for firmware flashing
There are two option for flashing the firmware. The first (and strongly recommended) is flashing it while it is plugged into and powered by the transmitter. The second is flashing it out of the transmitter (the power is supplied by the FTDI cable). The second option is very risky because if the 3.3V bridge jumper is not removed after flashing it will fry your RF module - you have been warned.
####Option 1: Flashing with Tx power
- Put the module in the Tx
- Place a jumper over the BOOT0 pins
- Connect your 3.3V/5V FTDI cable (USB - TTL serial) to Multiprotocol serial port (RX,TX,GND,5V).The multimodule RX pin connected to FTDI TX pin and multi TX pin connected to FTDI RX pin.Connect only TX and RX pins(2 pins),the power will be supplied by TX.
- In arduino IDE under the Tools -> Board: check that you have selected the Generic STM32F103C series board
- Under Tools -> Upload Method: select Serial
- Click "Upload" and the sketch will be uploaded normally.This is valid for all arduino versions.
- Once the firmware has uploaded, remove the BOOT0 jumper.
####Option 2: Flashing without Tx power
The key difference of this method is that the 3.3V FTDI cable must also provide power to the 5V circuitry during the flashing process. To do this, a jumper must be enabled connecting the 3.3V VCC to the 5V line.
If the module is powered through the transmitter and this jumper is enabled, then it will feed 5V throughout the 3.3V circuit and this will fry your RF modules.
- Set BOOT0 jumper
- Set the 3.3V jumper.This step only for 3.3V USB-serial!!!.Skip this step if using 5V USB-serial.
- Connect your 3.3V FTDI cable (USB - TTL serial) to Multiprotocol serial port (RX,TX,GND,5V).If set 3.3V jumper ,3.3V supply from USB-serial goes to 5V pin.
- In arduino IDE under the Tools -> Board: check that you have selected the Generic STM32F103C series board
- Under Tools -> Upload Method: select Serial.
- Click "Upload" and the sketch will be uploaded normally.
- Once the firmware has uploaded:
- Remove the 3.3V jumper!!!!
- Remove the BOOT0 jumper
- Check that you removed the 3.3V jumper
###Flashing binary file: If you want to flash a pre-compiled binary file (like the Release .bin files) you need specialized software and the FTDI cable.
- Set BOOT0 jumper
- Connect your 3.3V FTDI cable (USB - TTL serial) to Multiprotocol serial port (RX,TX,GND,5V)
- The other steps regarding power supply the same as previous recommandation regarding jumpers. For uploading binaries(.bin files) there is a specialized software you need to install on your computer.
Windows:
Download the ST Flash Loader Demonstrator from here: http://www.st.com/content/st_com/en/products/development-tools/software-development-tools/stm32-software-development-tools/stm32-programmers/flasher-stm32.html
Run the ST Flash Loader program. There are many tutorials on the web on how to use this program.For example
OSX:
To be checked.
###Report issues for the STM32 board You can report your problem using the GitHub issue system or go to the Main thread on RCGROUPS to ask your question. Please provide the following information:
- Multiprotocol code version
- STM32 version
- TX type
- Using PPM or Serial, if using er9x or ersky9x the version in use
- Different led status (multimodule and model)
- Explanation of the behavior and reproduction steps